Thermal Inkjet vs. Continuous Inkjet: How to Choose the Right Printer for Your Needs
Explore the key differences between thermal inkjet (TIJ) and continuous inkjet (CIJ) printing technologies, helping you determine the right printer for your needs.
Printing technology has evolved significantly, with thermal inkjet (TIJ) and continuous inkjet (CIJ) printers leading the charge in industrial, commercial, and even consumer applications. While both technologies serve the same ultimate purpose—applying text, codes, or graphics onto a substrate—their underlying mechanisms, advantages, and limitations differ considerably. Choosing the right printer for your needs requires a thorough understanding of these differences.
In this comprehensive guide, we’ll dive deep into the thermal inkjet vs continuous inkjet debate, comparing their functionalities, benefits, and drawbacks to help you make an informed decision.
Understanding the Basics of Thermal Inkjet and Continuous Inkjet
What is Thermal Inkjet Printing?
Thermal inkjet (TIJ) technology uses heat to create ink droplets. Inside the printer’s printhead, a heating element rapidly warms a tiny volume of ink to create a vapor bubble. This bubble expands and ejects an ink droplet through the nozzle, which then lands on the substrate. Once the droplet is expelled, the bubble collapses, allowing the chamber to refill with ink for the next cycle.
Advantages of TIJ Printing:
- High Resolution: TIJ printers excel in delivering high-quality prints, often at resolutions of 600 dpi or more, making them suitable for fine details like barcodes and logos.
- Compact Design: These printers are lightweight and portable, ideal for applications where space is limited.
- Ease of Use: TIJ systems are user-friendly, with straightforward cartridge replacements and minimal setup requirements.
Disadvantages of TIJ Printing:
- Limited Ink Options: TIJ systems often use water-based inks, which may not adhere well to non-porous surfaces like plastics or metals.
- Lower Speed: While they produce high-quality prints, TIJ printers are not designed for high-speed operations, making them less suitable for industrial environments.

What is Continuous Inkjet Printing?
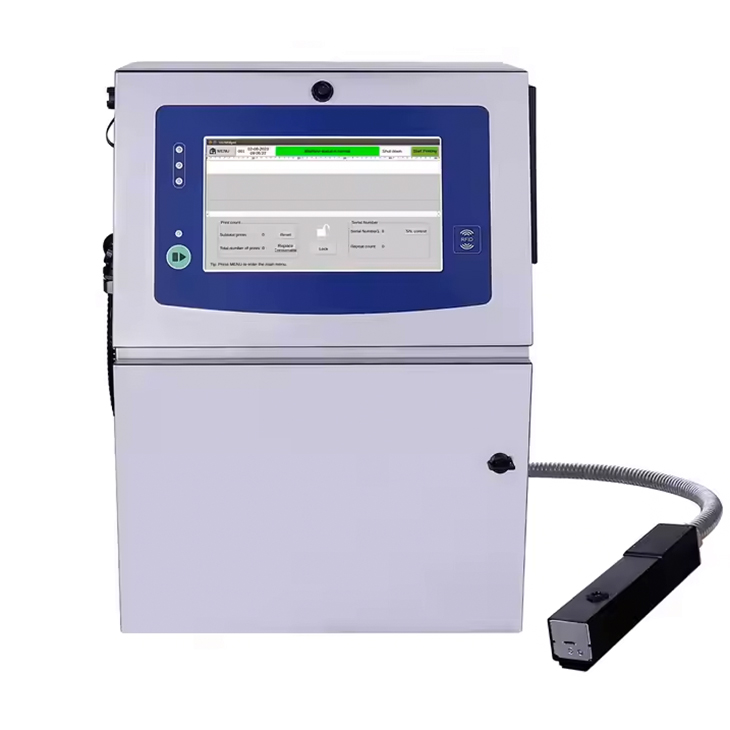
Continuous inkjet (CIJ) technology operates by forcing liquid ink through a nozzle to create a continuous stream of droplets. Vibrations from a piezoelectric crystal break the stream into tiny, uniformly sized droplets. An electric charge is applied to selected droplets, which are then deflected by an electrostatic field to form the desired print pattern. Unused droplets are collected and recirculated for efficiency.
Advantages of CIJ Printing:
- High-Speed Printing: CIJ systems can print at impressive speeds, making them ideal for large-scale operations like food packaging and product coding.
- Versatility: CIJ printers can handle a wide range of substrates, including curved, uneven, and non-porous surfaces.
- Durability in Harsh Environments: These printers are built to perform reliably in challenging industrial settings with dust, moisture, or high temperatures.
Disadvantages of CIJ Printing:
- Higher Initial Cost: CIJ printers are more expensive to purchase and install than TIJ systems.
- Maintenance Requirements: Regular cleaning and servicing are necessary to prevent nozzle clogs and maintain optimal performance.
Comparing Thermal Inkjet vs Continuous Inkjet
1. Print Quality
- Thermal Inkjet: With its ability to achieve resolutions of up to 600 dpi or more, TIJ printers produce sharp, detailed images and text. This makes them perfect for applications like pharmaceutical labels, where precision is critical. However, the high resolution may not be as noticeable on large-scale or high-speed operations.
- Continuous Inkjet: CIJ printers typically operate at lower resolutions, around 200-300 dpi. While this is sufficient for basic text, logos, and codes, it may not meet the demands of industries requiring fine details. However, their ability to print consistently on uneven surfaces is a significant advantage.
2. Speed and Volume
- Thermal Inkjet: TIJ printers are best suited for low- to medium-volume jobs. Their slower printing speed compared to CIJ makes them ideal for small-scale operations like boutique packaging or office use.
- Continuous Inkjet: CIJ printers are designed for high-speed, continuous operation. They can print thousands of products per hour without compromising efficiency, making them the preferred choice for industries like beverage bottling and food processing.
3. Substrate Compatibility
- Thermal Inkjet: TIJ printers excel on porous surfaces such as paper and cardboard. While some specialized TIJ systems can handle non-porous materials with modified inks, their compatibility is generally limited compared to CIJ.
- Continuous Inkjet: CIJ printers can print on virtually any surface, including plastic, glass, metal, rubber, and wood. This versatility is invaluable in industries requiring diverse substrate printing.
4. Maintenance and Downtime
- Thermal Inkjet: TIJ systems require minimal maintenance. Cartridge replacement is straightforward, and there’s no need for frequent cleaning. However, the frequent replacement of cartridges can lead to interruptions in high-volume operations.
- Continuous Inkjet: CIJ systems demand regular cleaning and maintenance to prevent nozzle clogs and ink buildup. While this can be time-consuming, it ensures the system operates smoothly over extended periods.
5. Cost Considerations
- Thermal Inkjet: TIJ printers are generally more affordable upfront, with lower initial investment costs. However, the ongoing expense of replacing ink cartridges can accumulate over time, especially in high-volume settings.
- Continuous Inkjet: CIJ printers have higher initial costs but are more cost-efficient for large-scale operations. Their ink recirculation system reduces waste, lowering long-term operating expenses.
6. Environmental Impact
- Thermal Inkjet: Many TIJ systems use water-based inks, which are less harmful to the environment compared to solvent-based inks. However, the frequent replacement of cartridges generates more waste.
- Continuous Inkjet: CIJ printers often use solvent-based inks, which can be less environmentally friendly. However, advancements in ink technology have led to more sustainable options, such as biodegradable and low-VOC (volatile organic compound) inks.
Applications of Thermal Inkjet vs Continuous Inkjet
Thermal Inkjet Applications:
Pharmaceutical Industry: TIJ printers provide precise and legible codes, crucial for regulatory compliance and product safety.
Retail Packaging: Ideal for printing high-quality labels and barcodes on small packaging.
Office Use: Perfect for producing high-resolution documents and promotional materials.
Continuous Inkjet Applications:
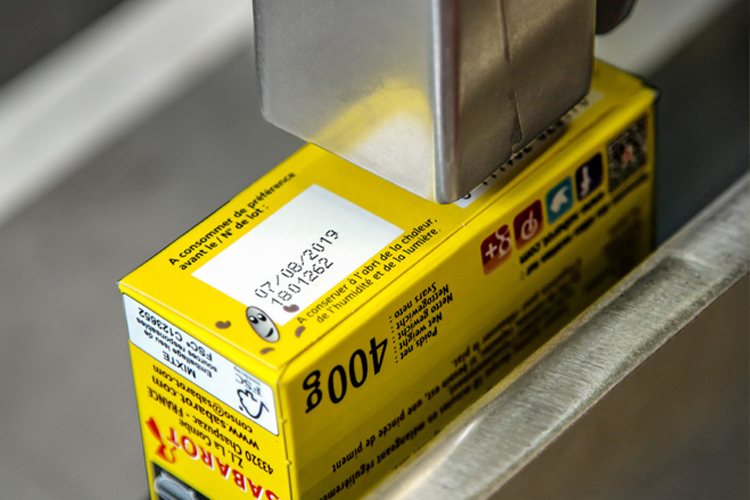
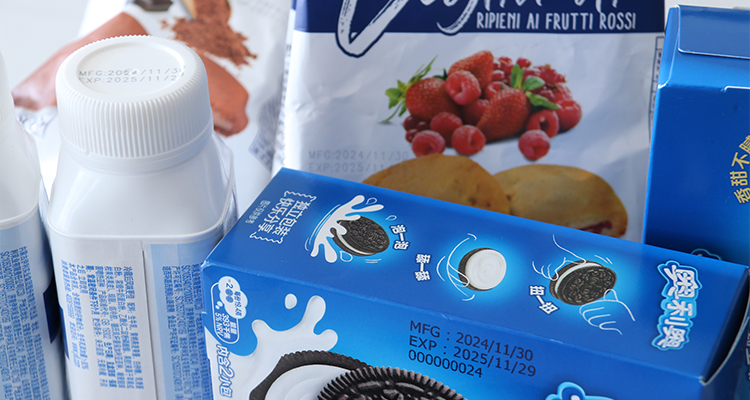
Food and Beverage Packaging: CIJ printers can print batch codes, expiration dates, and logos on bottles, cans, and flexible packaging.
Automotive Parts: Suitable for marking parts with serial numbers or manufacturing codes.
Harsh Industrial Environments: CIJ systems perform reliably in factories and warehouses with challenging conditions.

Factors to Consider When Choosing Between TIJ and CIJ
When deciding between thermal inkjet vs continuous inkjet, consider the following:
- Volume Requirements: If your operation involves high-speed, high-volume printing, CIJ is the better choice. For smaller, detail-oriented jobs, TIJ is more appropriate.
- Substrate Type: TIJ is ideal for porous materials, while CIJ’s versatility allows it to print on nearly any surface.
- Budget: TIJ is cost-effective for small-scale operations, while CIJ offers better long-term value for large-scale production.
- Environmental Impact: TIJ’s water-based inks may align better with sustainability goals, while CIJ offers eco-friendly ink options in certain models.
- Maintenance Capabilities: TIJ requires less maintenance, making it user-friendly, while CIJ demands regular servicing to ensure optimal performance.
Conclusion
The choice between thermal inkjet vs continuous inkjet depends on your specific printing needs. For businesses prioritizing high resolution, ease of use, and affordability, TIJ is a reliable option. On the other hand, CIJ is unmatched in speed, substrate versatility, and suitability for industrial-scale operations.
By evaluating factors such as print quality, speed, substrate compatibility, and cost, you can select the technology that aligns with your business goals. Whether you’re printing pharmaceutical labels, food packaging, or automotive parts, understanding the strengths and limitations of TIJ and CIJ will help you make a strategic investment in your printing capabilities.