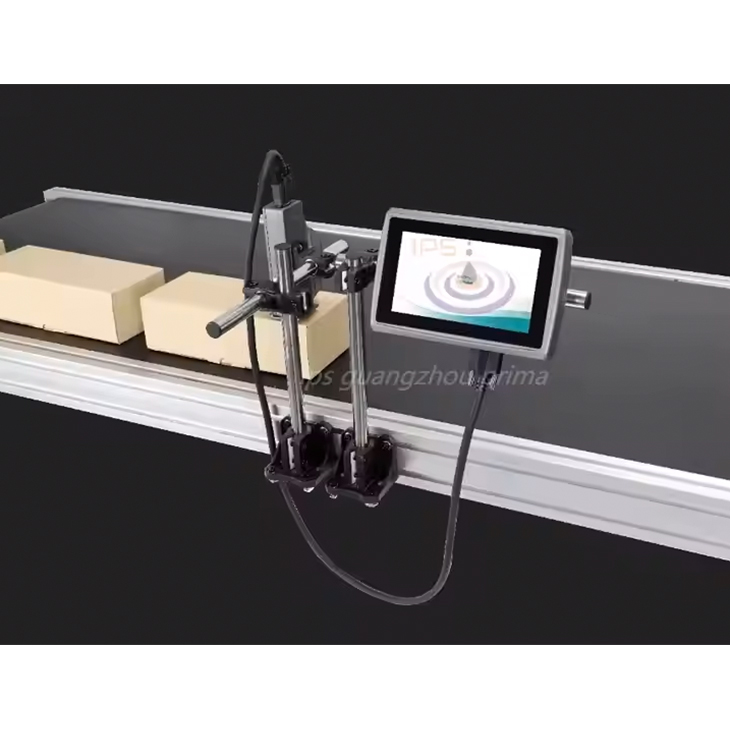
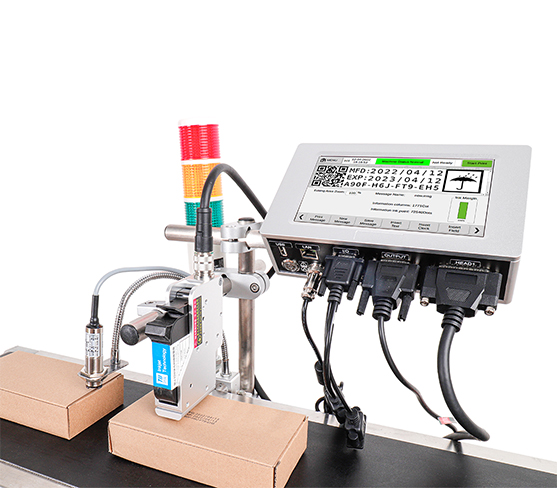
What is a Thermal Inkjet Printer? A Comprehensive Guide to Industrial Thermal Inkjet Printers
Explore the fundamentals of thermal inkjet printers, their applications, and why they are such an asset to the industrial sector.
In the world of industrial printing, efficiency, precision, and speed are paramount. Thermal inkjet printing (TIJ) technology has carved out a significant place for itself in industries that demand high-quality, fast, and reliable printing solutions. From packaging to labeling, to product coding, thermal inkjet printers are a popular choice for businesses that need cost-effective, versatile, and high-speed printing options. This blog will explore the fundamentals of thermal inkjet printers, their applications, and why they are such an asset to the industrial sector.
Understanding Thermal Inkjet Technology
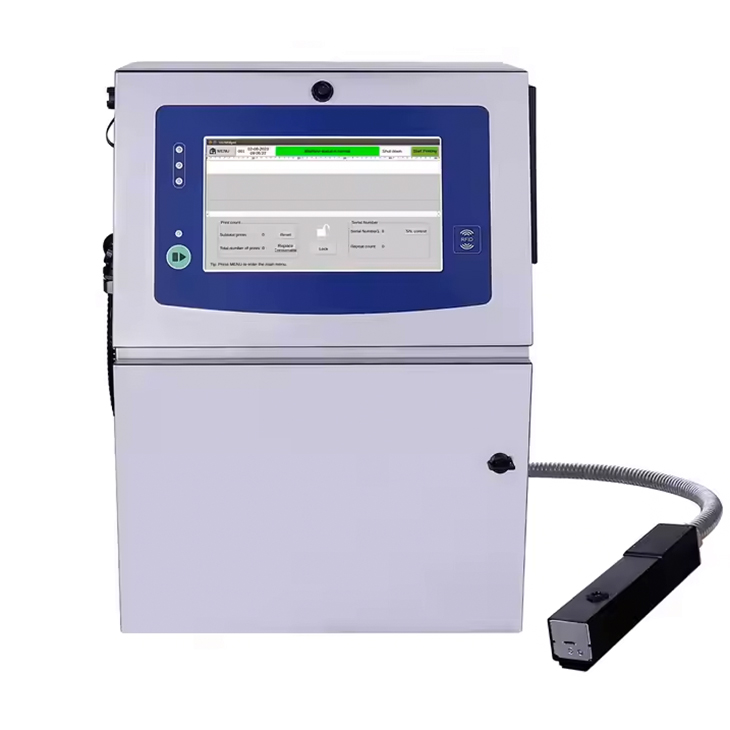
What is a Thermal Inkjet Printer?
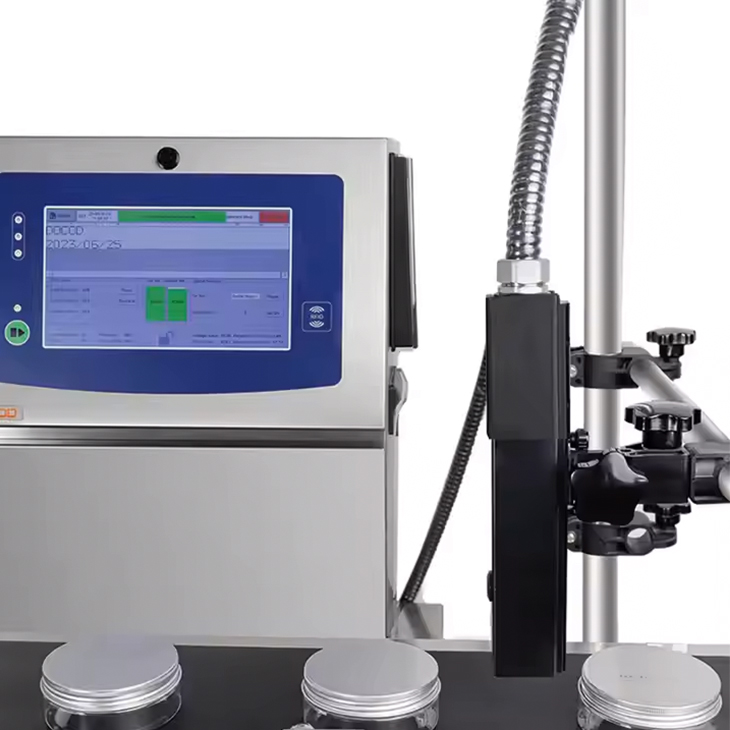
A thermal inkjet printer, commonly referred to as a TIJ printer, uses heat to create precise, controlled droplets of ink, which are then sprayed onto the printing surface. The heart of the technology lies in its use of tiny heating elements that vaporize the ink, forcing it through microscopic nozzles. When heated, the ink inside the printhead expands, forming a bubble. As the bubble bursts, it propels a droplet of ink onto the substrate, creating the printed image or text.
The term “thermal inkjet” distinguishes this printing method from other types of inkjet printers, such as piezoelectric inkjet printers, which rely on mechanical pressure to eject ink. In contrast, thermal inkjet technology utilizes heat to control the ink flow, offering specific benefits in terms of print quality and speed.
How Does Thermal Inkjet Printing Work?
The working mechanism of thermal inkjet printers can be broken down into a few simple steps:
- Ink Supply: Ink is stored in a cartridge that is connected to the printhead. The ink is typically a water-based solution, although variations exist for specific applications.
- Heating Element Activation: Each nozzle in the printhead contains a small heating element. When the printer receives a command to print, electrical signals trigger these elements to heat up.
- Formation of Ink Droplet: The heating element rapidly heats the ink, causing it to expand. This creates a bubble of vapor inside the printhead.
- Ink Ejection: As the vapor bubble bursts, the ink is forced through a tiny nozzle, creating a droplet of ink that lands on the paper or packaging material below.
- Controlled Placement: The printhead moves across the material, precisely placing ink droplets in the correct pattern to form text or images.
This method is highly efficient and can produce sharp, vibrant prints, making it ideal for high-volume printing applications.
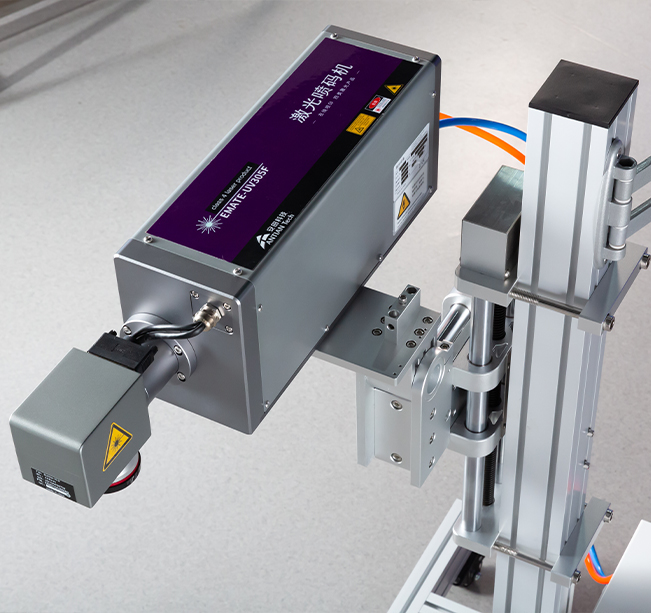

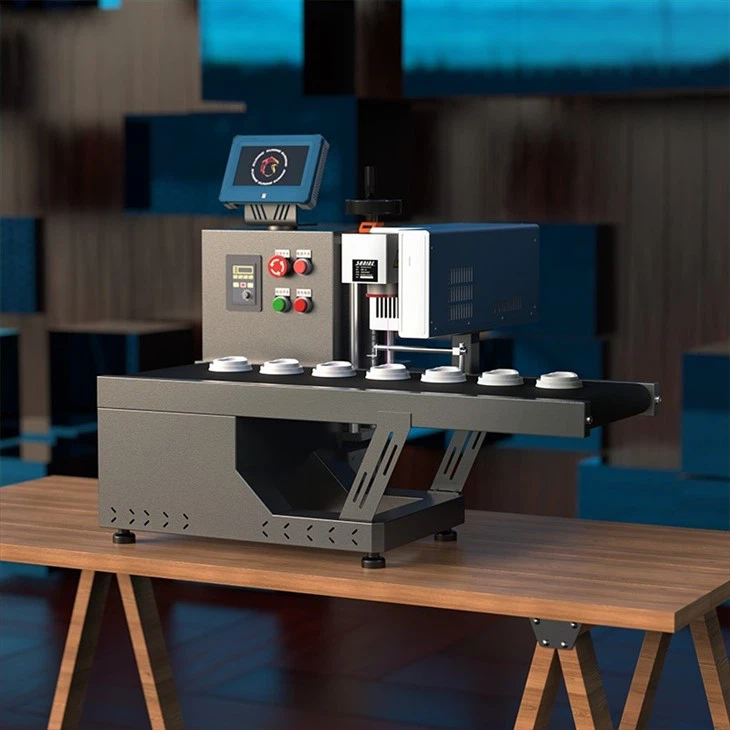
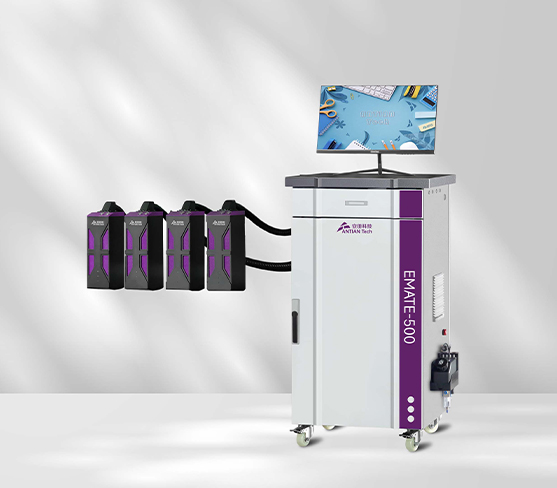
Industrial Thermal Inkjet Printers
The Role of Industrial Thermal Inkjet Printers
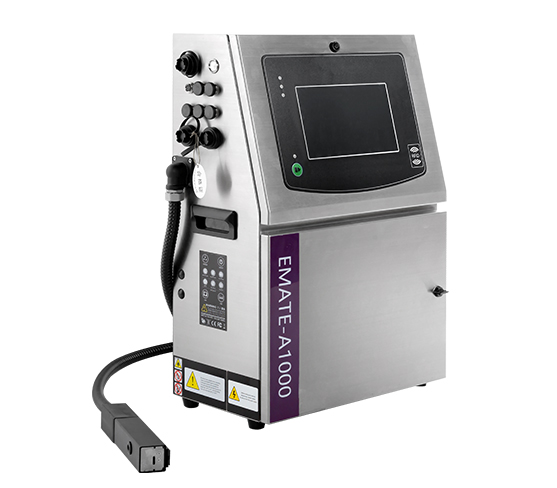
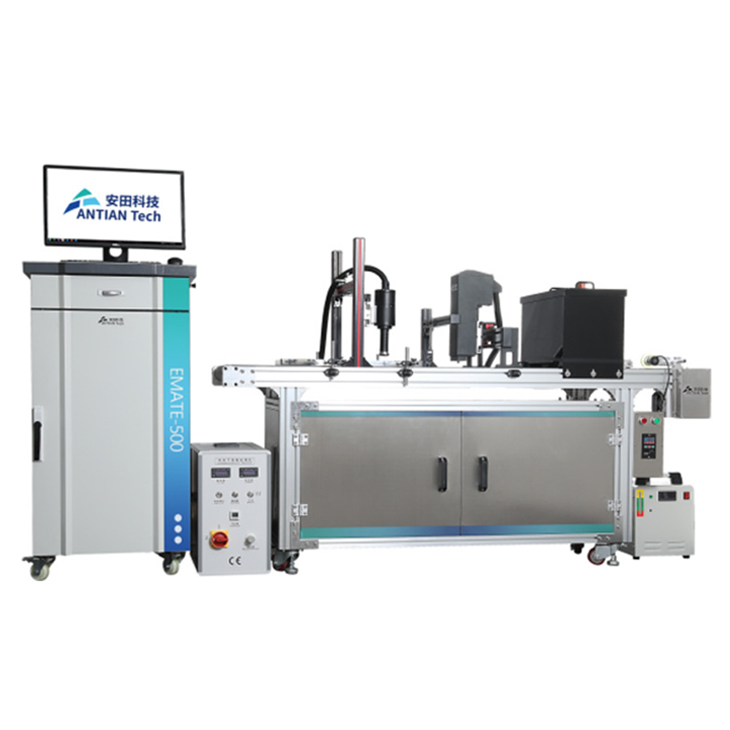
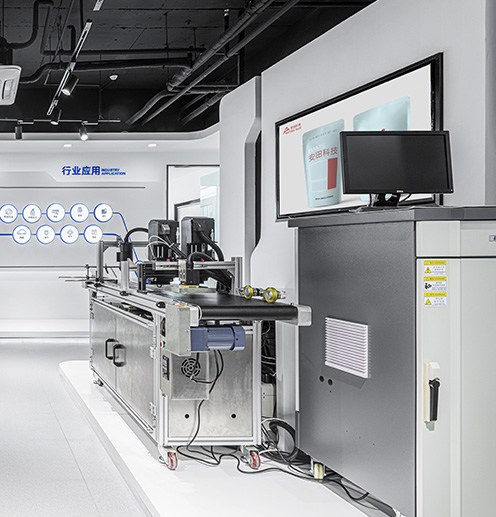
Industrial thermal inkjet printers are specifically designed for high-performance, high-volume printing in demanding environments. They are commonly used in industries such as manufacturing, packaging, and logistics, where fast, accurate, and reliable printing is necessary for product identification, date coding, labeling, and barcoding. The ability of industrial TIJ printers to print on various substrates, including plastics, metals, and paper, makes them highly versatile for different industrial applications.
Here’s a deeper look into the key characteristics of industrial thermal inkjet printers:
- High-Speed Printing: Industrial thermal inkjet printers are capable of printing at high speeds, ensuring that production lines are not slowed down. The technology is designed to keep up with fast-paced manufacturing processes, providing rapid print results.
- Precision and Quality: TIJ printers deliver precise, high-resolution prints, making them ideal for tasks requiring fine details, such as QR codes, barcodes, and logos. Their print quality rivals that of laser printers, making them a top choice for industries that demand superior print accuracy.
- Low Maintenance: One of the advantages of industrial thermal inkjet printers is their relatively low maintenance compared to other types of industrial printers. They have fewer moving parts, which reduces the need for frequent servicing and downtime.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Thermal inkjet printers offer a cost-effective solution due to their low initial investment and lower ongoing maintenance costs. The ink cartridges are typically less expensive than the toner used in laser printers, and the printheads have a long lifespan, further lowering the total cost of ownership.
- Eco-Friendly: Since thermal inkjet printing does not require solvents or other hazardous chemicals, it is considered an eco-friendly option compared to other types of industrial printing. This makes it a sustainable choice for industries focused on reducing their environmental footprint.
Applications of Industrial Thermal Inkjet Printers
Thermal inkjet technology has a broad range of industrial applications. Here are some of the key areas where TIJ printers are commonly used:
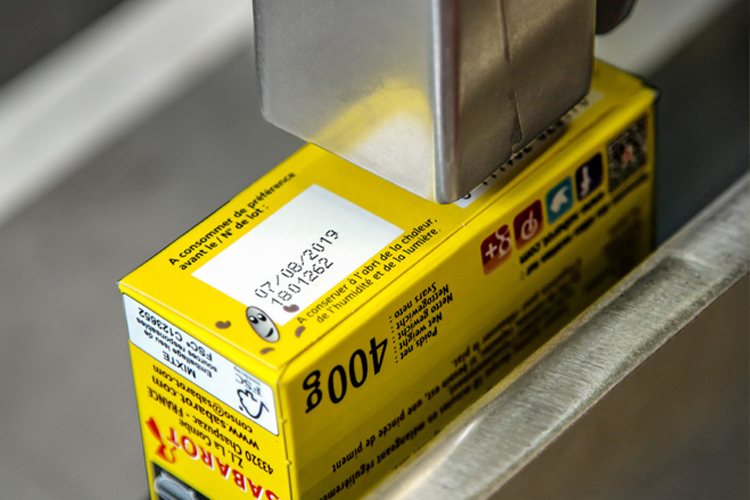
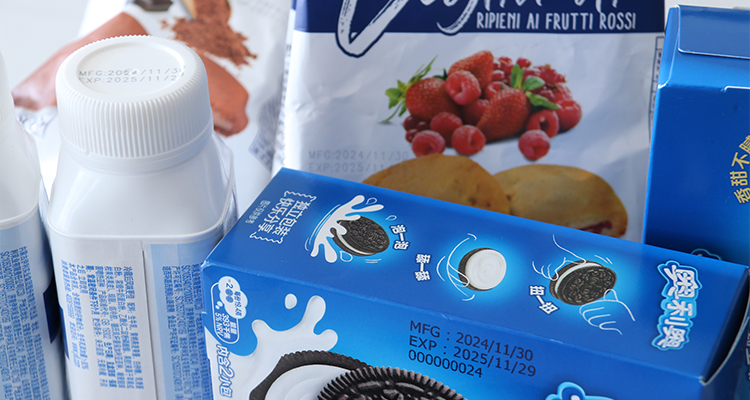
- Product Coding: Thermal inkjet printers are widely used for coding products with important information such as expiration dates, batch numbers, or manufacturing codes. This is particularly critical in industries such as food and pharmaceuticals, where accurate and legible product coding is essential for traceability and safety.
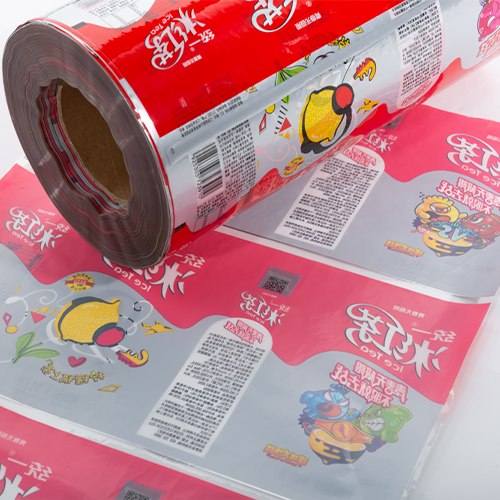
- Packaging: In the packaging industry, TIJ printers are used to print labels, barcodes, and QR codes directly onto boxes, bottles, or other packaging materials. This provides essential product information while allowing for rapid and accurate printing on a variety of surfaces.
- Labeling: Thermal inkjet printers are also used in the labeling industry to print custom labels with high-resolution text, graphics, and barcodes. Their ability to print on different types of materials such as paper, film, and plastics makes them versatile for various labeling applications.
- Direct Part Marking: TIJ printers are used to mark products directly, such as part numbers, serial numbers, and logos, without the need for separate labels. This is especially useful in automotive and electronics industries where durability and legibility are crucial.
- Logistics and Distribution: Thermal inkjet printers are vital in logistics for printing shipping labels, handling information, and barcodes, ensuring smooth and efficient distribution processes.
Key Advantages of Thermal Inkjet Printers
- High-Resolution Prints: Thermal inkjet technology is known for delivering high-resolution prints, with some printers offering up to 600 dpi. This makes them perfect for printing fine details, such as small text, logos, and barcodes.
- Flexibility: These printers can print on a variety of materials, including paper, corrugated cardboard, plastics, and metals. This makes them suitable for industries like packaging, electronics, and manufacturing.
- Minimal Ink Smearing: Since thermal inkjet printers use quick-drying ink, there is less chance of smearing or smudging during or after the printing process. This ensures the print quality remains intact throughout the handling and shipping process.
- Easy Integration: Industrial thermal inkjet printers can be easily integrated into existing production lines. With their compact design and user-friendly interfaces, these printers can seamlessly blend into the manufacturing workflow.
- Reduced Downtime: With fewer moving parts and minimal maintenance requirements, industrial TIJ printers help reduce operational downtime, keeping production lines running smoothly.
- Quick Setup: TIJ printers require little warm-up time, meaning they can start printing immediately after being turned on. This is particularly valuable in fast-paced production environments.

Challenges of Thermal Inkjet Printers
While thermal inkjet printers offer several benefits, they are not without their limitations:
- Ink Limitations: Thermal inkjet printers typically use water-based inks, which may not be suitable for all applications. In some industries, such as the automotive or chemical sectors, the ink may not provide the durability required.
- Printhead Cost: While the printheads of thermal inkjet printers have a long lifespan, replacing them can be costly, especially in high-volume printing operations.
- Environmental Sensitivity: Thermal inkjet printing is sensitive to environmental conditions such as humidity and temperature, which can affect print quality. This may be a concern in certain industrial settings where environmental control is difficult.
- Limited Print Speed for Large-Scale Jobs: While TIJ printers are fast, they may not be as suitable for extremely high-volume applications as some other types of industrial printers, such as continuous inkjet printers.
Conclusion
Thermal inkjet printers have established themselves as a reliable and efficient printing technology for industrial applications. Offering high-speed, high-resolution, and versatile printing capabilities, TIJ printers are an excellent choice for businesses looking to improve their product coding, packaging, labeling, and direct part marking processes. Their cost-effectiveness, ease of maintenance, and eco-friendly design make them a valuable asset to industries worldwide. Whether you're in food production, pharmaceuticals, or logistics, a thermal inkjet printer can meet your needs for high-quality printing while minimizing environmental impact and operational costs.
As thermal inkjet technology continues to evolve, we can expect even greater improvements in print quality, speed, and versatility, making it an essential tool for modern industrial printing needs.