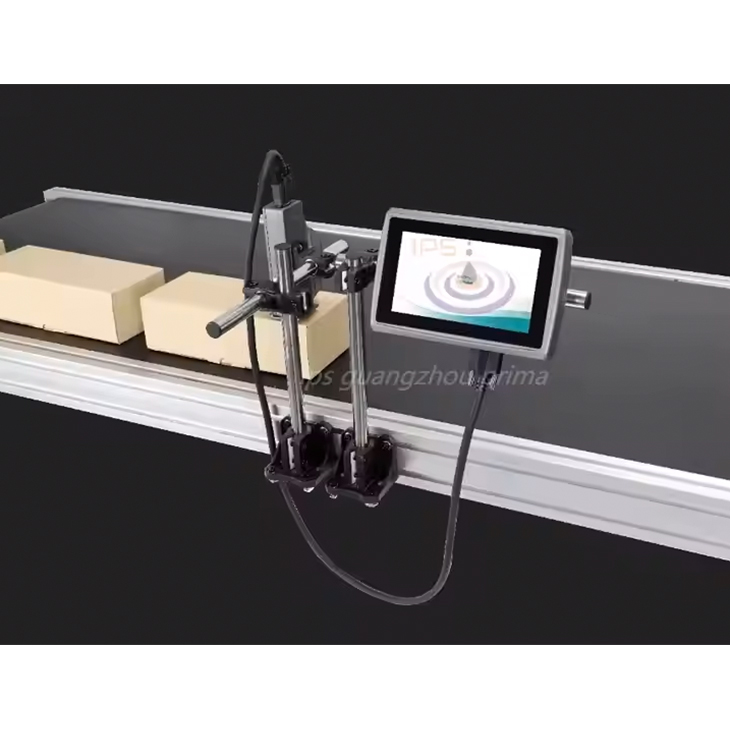
What Is Thermal Inkjet Coder And How To Use It
Learn how thermal inkjet coder use heat and precision to deliver high-resolution printing for product labeling and marking across various industries.
In the modern manufacturing landscape, product labeling and marking are essential components of the production process. As industries demand more precise, reliable, and cost-effective ways to mark products, the thermal inkjet coder has emerged as a leading solution. Thermal inkjet coding offers numerous advantages over traditional methods, such as versatility, ease of use, and high-quality output. This article provides an in-depth look at thermal inkjet coders, their working mechanism, applications, benefits, and how to use them effectively in a production setting.
What Is a Thermal Inkjet Coder?
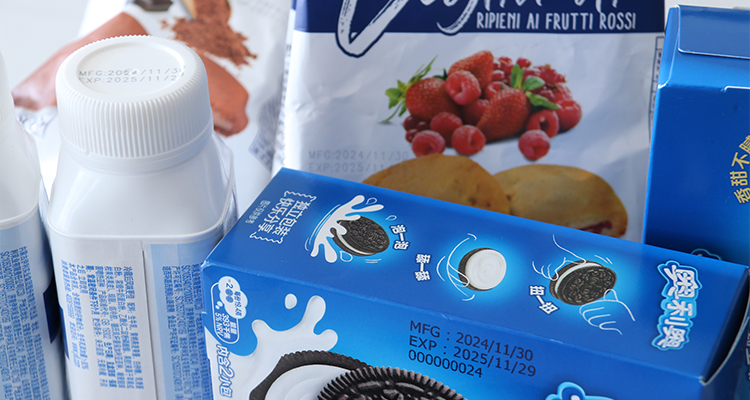
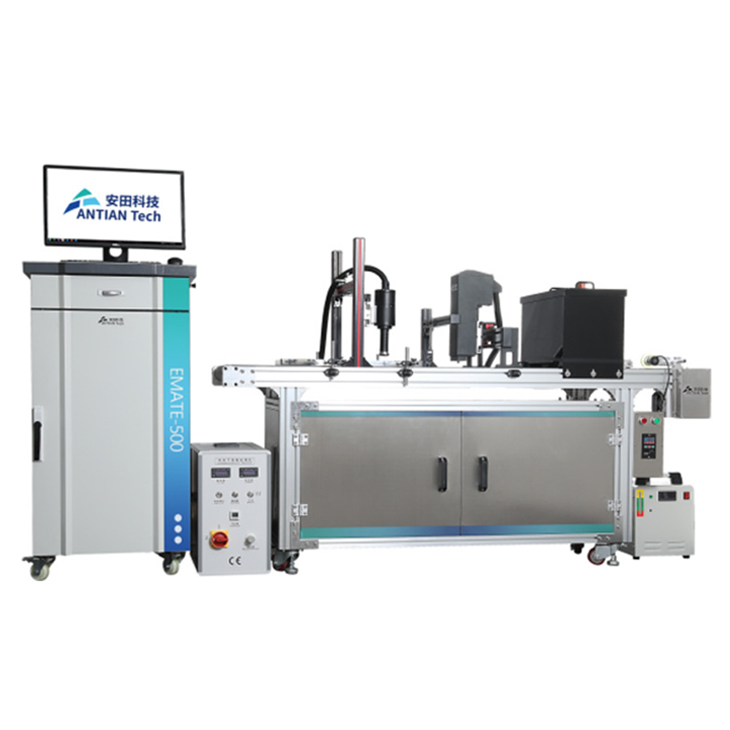
A thermal inkjet coder is a specialized printing device used for applying codes, batch numbers, expiry dates, logos, barcodes, and other types of variable data onto products or packaging. It operates by using heat to force ink droplets from a cartridge onto a surface, forming a printed image or text. These coders are highly adaptable and can be used on a variety of materials, including paper, plastic, metal, glass, and even some non-porous surfaces.
The main technology behind thermal inkjet coding involves microscopic nozzles that release ink droplets when heated. This allows for very high precision, enabling the coder to print small text and detailed images, such as QR codes, serial numbers, and logos. Thermal inkjet coders are commonly used in industries like food and beverage, pharmaceuticals, cosmetics, electronics, and packaging due to their efficiency and ability to produce clear, readable codes at high speeds.
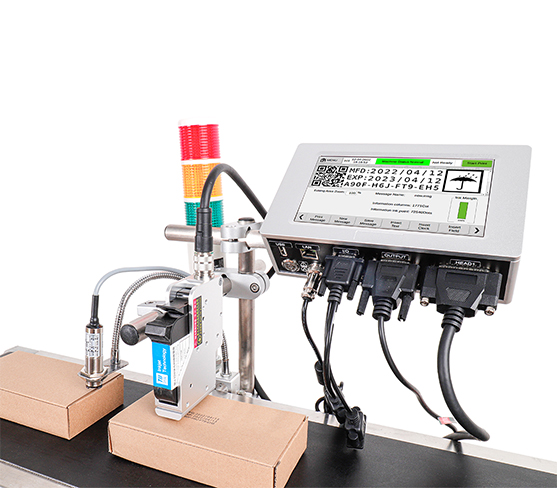
How Does Thermal Inkjet Coding Work?
Understanding how thermal inkjet coding works involves delving into the core technology of the device. Here's a detailed breakdown of the process:
Heating Element Activation:
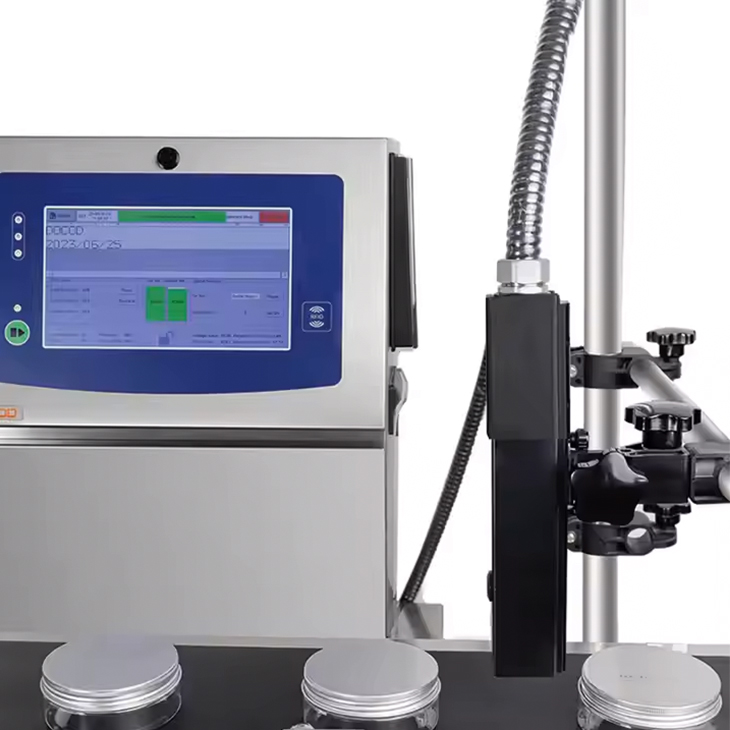
Thermal inkjet coders consist of a printhead with a series of small nozzles. Each nozzle contains a tiny heating element that is controlled electronically. When a print command is issued, the heating element rapidly heats up. This heating action is triggered by an electrical signal sent from the coder’s processor.
Ink Heating:
The heat from the element vaporizes the ink inside the nozzle chamber. The ink used in thermal inkjet coding is usually a liquid that is designed to react to heat, causing it to form a small bubble of vapor. This bubble builds up pressure within the nozzle.
Ink Droplet Formation:
As the vapor bubble forms, it forces a precise droplet of ink out of the nozzle and onto the substrate (the surface being printed on). The ink droplets are incredibly small—typically in the range of picoliters (one trillionth of a liter)—allowing for high-resolution prints.
Substrate Marking:
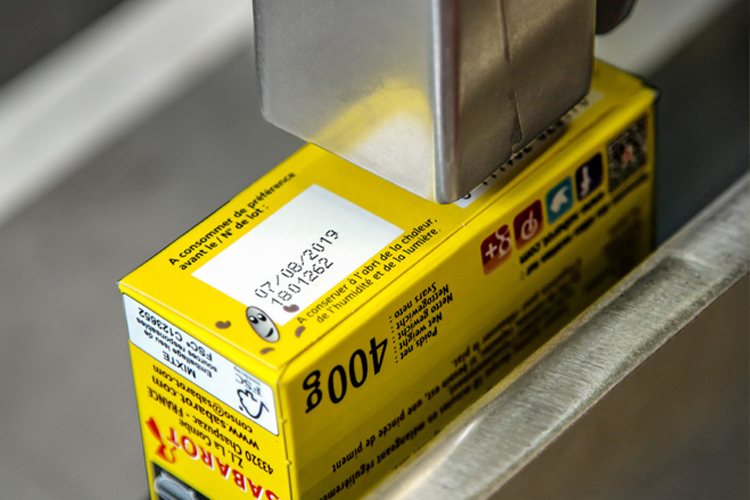
The ink droplets land on the substrate in a highly controlled pattern. These droplets form characters, images, barcodes, or any other variable data as required by the user. The printhead moves across the surface, and the droplets are ejected rapidly to create the desired output.
Drying and Curing:
After the ink is applied to the substrate, it typically dries almost immediately, thanks to the quick evaporation of the ink solvent. Some thermal inkjet coders use special drying technologies, like UV light or heat, to ensure the ink sets and adheres well to the surface.
Benefits of Using a Thermal Inkjet Coder
The popularity of thermal inkjet coders in various industries can be attributed to several key benefits that they offer over traditional printing methods:
- High-Resolution Printing:
One of the standout features of thermal inkjet coding is its ability to print at extremely high resolutions. Modern thermal inkjet coders can achieve print resolutions of up to 600 dpi (dots per inch), which is ideal for printing detailed information like small text, barcodes, and QR codes. This clarity ensures that products are accurately labeled, improving traceability and compliance with regulations. - Versatile Substrate Compatibility:
Thermal inkjet coders are compatible with a wide range of substrates, including both porous and non-porous materials. Whether you need to print on paper, plastic, glass, or metal, a thermal inkjet coder can handle it. This versatility makes it a great choice for industries that deal with diverse packaging materials. - Low Maintenance:
Thermal inkjet coders are known for their minimal maintenance requirements. Unlike traditional printing technologies that may have complex components like rollers or ribbons, thermal inkjet printers rely on ink cartridges that are easy to replace. The lack of moving parts also reduces the likelihood of mechanical breakdowns, making it a more reliable option in high-speed production environments. - Eco-Friendly Options:
Many thermal inkjet coders use water-based inks that are safer for the environment than solvent-based inks. These inks are less toxic and can be disposed of more easily. In addition, some thermal inkjet coders use biodegradable inks, further reducing their environmental impact. - Compact and User-Friendly:
Thermal inkjet coders are typically smaller and more compact than other industrial printing devices, making them easier to integrate into existing production lines. Their user-friendly interfaces also simplify operation, with touchscreens or software that allow for quick setup and easy programming of print jobs.
Applications of Thermal Inkjet Coding
Thermal inkjet coding is widely used across various industries for its ability to deliver high-quality, precise prints. Some of the most common applications include:
Food and Beverage Industry:
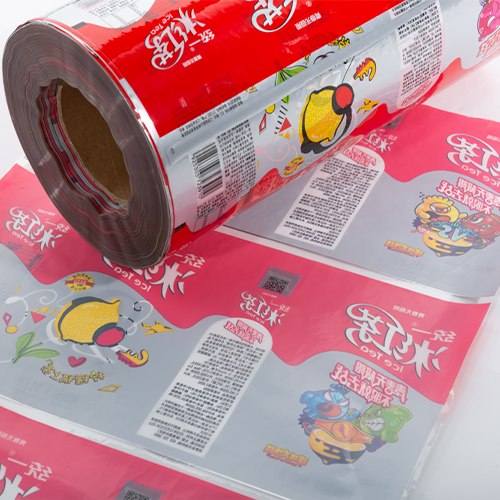
In this industry, thermal inkjet coders are used to print essential information like expiration dates, batch numbers, and best-before dates on food packaging. These codes are crucial for ensuring product safety and meeting regulatory requirements. Thermal inkjet coding can also be used to print barcodes and QR codes for inventory tracking and traceability.
Pharmaceutical Industry:
The pharmaceutical sector requires highly accurate and reliable printing for batch numbers, expiration dates, and lot codes. Thermal inkjet coders provide the high resolution and clarity needed for these critical applications. They are used to mark everything from blister packs to cartons and vials.
Electronics Industry:
Thermal inkjet coders are employed to print serial numbers, component codes, and logos on electronic devices, circuit boards, and cables. This ensures product traceability and quality control in the electronics manufacturing process.
Packaging Industry:
In the packaging sector, thermal inkjet coders are used to print product information, branding, safety warnings, and instructions directly onto packaging materials. Whether it's a cardboard box, plastic pouch, or shrink wrap, thermal inkjet coding provides a reliable and cost-effective solution.
Retail and Logistics:
Thermal inkjet coders are essential for marking products with barcodes, QR codes, and tracking numbers. This helps streamline inventory management and logistics operations, ensuring accurate stock tracking and efficient delivery processes.
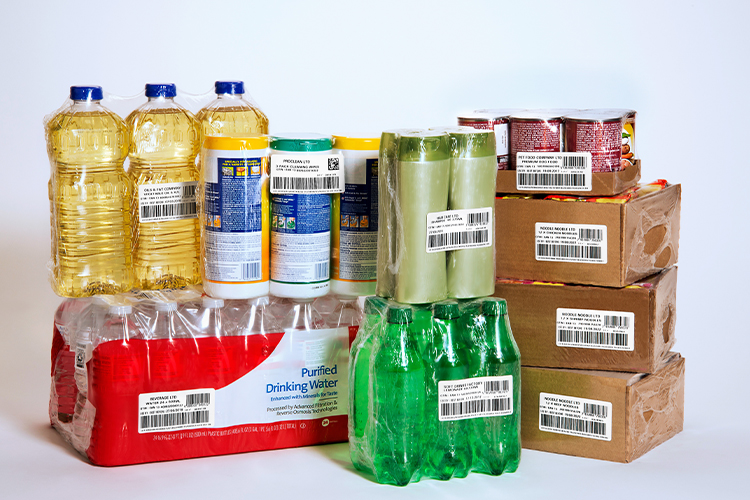

How to Use a Thermal Inkjet Coder
Proper usage of a thermal inkjet coder is essential to maximize its efficiency and ensure high-quality prints. Here’s a detailed guide on how to use a thermal inkjet coder effectively:
1. Setup and Installation
- Unpack and Position: When setting up a thermal inkjet coder, the first step is to unpack the unit and position it appropriately on the production line. Ensure that the printer is placed at the correct height and angle to align with the substrate for consistent printing.
- Power On: Once positioned, connect the coder to a power source and switch it on. The display panel or touchscreen will typically light up, indicating that the device is ready for use.
- Load Ink Cartridges: Install the appropriate ink cartridges for your production requirements. Most thermal inkjet coders use ink cartridges that are easily replaceable, making it simple to switch out inks when necessary.
2. Program the Coder
The next step is to program the coder with the required print job. Use the device’s control panel or a connected computer to input the text, graphics, barcodes, or other data that need to be printed. You can adjust settings like print speed, font size, and alignment, ensuring that the print job matches your specifications.
3. Test the Print
Before integrating the coder into full-scale production, run a test print. This ensures that the print quality meets your expectations and that the ink adheres well to the substrate. If needed, make adjustments to the settings or alignment to ensure the print is clear and legible.
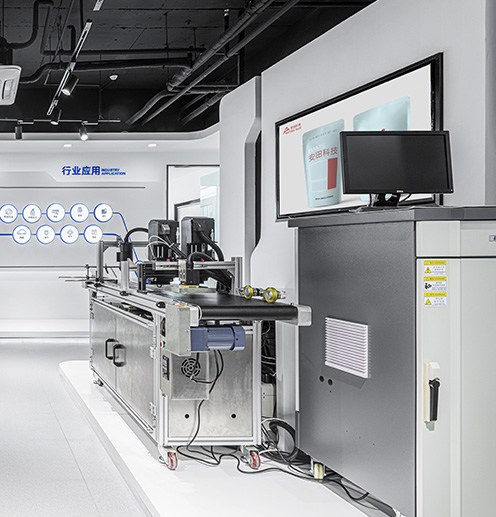
4. Integrate with the Production Line
Once the coder is properly programmed and tested, it’s time to integrate it into your production line. Most thermal inkjet coders are designed to work with conveyor belts, allowing them to print codes onto products as they pass by. Ensure that the printer is synchronized with the production speed to avoid printing errors.
5. Monitor Operation
Throughout the production process, it’s important to monitor the operation of the coder. Regularly check the print quality to ensure that the ink is being applied properly. Additionally, keep an eye on ink levels and replace cartridges when necessary to avoid production downtime.
Tips for Effective Thermal Inkjet Coding
To get the most out of your thermal inkjet coder, consider the following tips:
Choose the Right Ink
The choice of ink plays a significant role in the quality and durability of the print. Make sure the ink is compatible with your substrate. For example, use solvent-based inks for non-porous surfaces and water-based inks for porous materials like cardboard.
Maintain Proper Distance
The distance between the nozzle and the substrate affects print quality. Too close, and the ink may smear; too far, and the print may be faint. Always follow the manufacturer’s recommended nozzle-to-substrate distance.
Keep Cartridges Clean
Clogged nozzles can cause inconsistent printing. Regularly clean the cartridges and nozzles to prevent ink buildup. Some coders come with self-cleaning features, but manual cleaning may be necessary for heavy use.
Monitor Environmental Conditions
Temperature, humidity, and dust can all affect the performance of thermal inkjet coders. Keep the environment clean and maintain stable conditions to ensure optimal print quality.
Regular Calibration
Periodically calibrate the printer to ensure accurate alignment and print consistency. This is especially important when switching between different substrates or inks.
Conclusion
A thermal inkjet coder is a powerful tool for industries that require high-quality, reliable, and efficient printing for product labeling and marking. Whether you are printing expiration dates, batch numbers, or barcodes, thermal inkjet coding provides the precision and versatility needed to meet industry standards. With minimal maintenance requirements, high-resolution printing, and compatibility with a wide range of substrates, thermal inkjet coders are becoming an indispensable part of modern manufacturing processes. By understanding how to use them effectively and following best practices, businesses can enhance their productivity and ensure the consistent quality of their printed codes.