Thermal Inkjet vs. Laser Printer: Which is Right for Your Printing Needs?
Explore the critical differences between thermal inkjet and laser printers, helping you determine which technology best suits your printing needs. Delve into the mechanics of each printer type, their advantages and disadvantages, and key factors to consider, such as print quality, speed, cost of ownership, and media compatibility.
When it comes to selecting a printer that meets your specific requirements, the debate between thermal inkjet and laser printers often takes center stage. Each technology possesses its own unique set of advantages and disadvantages, which can significantly influence your choice depending on your printing needs. In this detailed guide, we will explore the intricacies of thermal inkjet vs. laser printer technologies, their functionalities, cost considerations, and suitability for various tasks. By the end of this comprehensive analysis, you will have a clearer understanding of which printer type aligns best with your specific printing requirements and lifestyle.
Understanding the Basics
What is a Thermal Inkjet Printer?
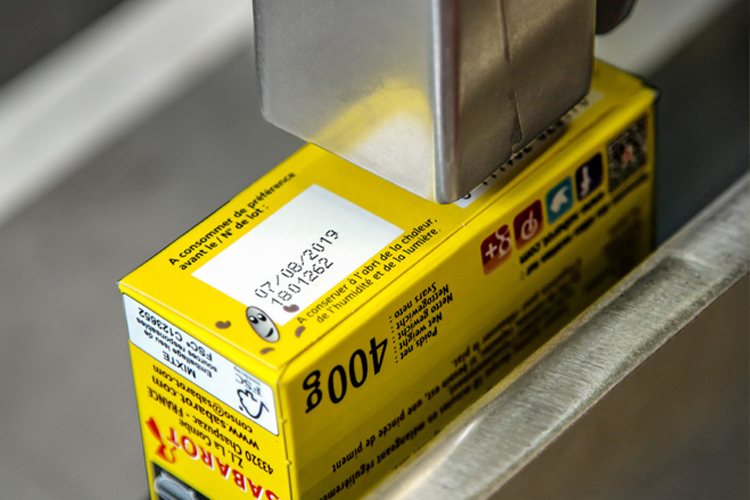
A thermal inkjet printer operates by using heat to vaporize liquid ink, producing tiny droplets that are ejected onto the paper to create images or text. This technology involves a specialized print head that contains a series of microscopic nozzles, each of which can spray ink in minute quantities. When printing, heating elements within the print head heat the ink in each nozzle, causing it to expand and form droplets that are precisely propelled onto the paper.

Advantages of Thermal Inkjet Printers:
1. High-Quality Output: Thermal inkjet printers are renowned for their ability to produce vibrant colors, rich gradients, and sharp text. This capability makes them particularly suitable for applications that require high-resolution images, such as photo printing, graphic design, and professional documents.
2. Versatility: These printers can accommodate a wide range of media types, including glossy photo paper, labels, cardstock, and envelopes. This adaptability makes thermal inkjet printers ideal for users who often switch between different printing tasks.
3. Affordability: Generally, thermal inkjet printers have a lower initial purchase price compared to their laser counterparts. This affordability can be particularly appealing for home users or small businesses operating on a tight budget.
Disadvantages of Thermal Inkjet Printers:
1. Speed Limitations: One of the primary drawbacks of thermal inkjet printers is their slower print speed compared to laser printers. This limitation can become evident when printing larger documents or when high-volume printing is required.
2. Ink Costs: Although the upfront cost may be low, the long-term expense of replacement ink cartridges can be substantial. Frequent printing can lead to a high consumption of ink, increasing overall operational costs.
3. Durability Concerns: Documents produced with thermal inkjet printers may be susceptible to smudging if they are not allowed to dry adequately. Additionally, the ink can fade over time, especially if exposed to sunlight or moisture, which may be a consideration for archival purposes.
What is a Laser Printer?
A laser printer employs a completely different technology based on electrostatics and heat. This printer utilizes a laser beam to transfer toner, which is a fine powder, onto the paper. The process begins with the laser creating an electrostatic image of the desired print on a rotating drum. Once the drum is charged, toner is applied to the areas that have been affected by the laser. The toner is then transferred onto the paper and fused by applying heat, resulting in a finished printed page.

Advantages of Laser Printers:
1. Speed and Efficiency: Laser printers are renowned for their speed, often producing pages at a rate that significantly surpasses that of thermal inkjet printers. This makes them particularly suitable for environments where high-volume printing is essential, such as corporate offices and print shops.
2. Cost Efficiency: Although the initial investment in a laser printer may be higher, the cost per page is often considerably lower than that of thermal inkjet printers, particularly for black-and-white documents. This efficiency is due to the longer life of toner cartridges, which can yield a significantly larger number of prints compared to ink cartridges.
3. Durability of Prints: Documents printed using laser technology are generally more resistant to smudging and fading over time. The fusion process used in laser printing ensures that the toner adheres strongly to the paper, making it suitable for archival purposes and documents that will be handled frequently.
Disadvantages of Laser Printers:
1. Higher Initial Investment: The upfront cost of a laser printer can be significantly greater than that of a thermal inkjet printer. For budget-conscious consumers or small businesses, this higher price point can be a deterrent.
2. Color Accuracy Limitations: While color laser printers are available, they may not achieve the same level of color accuracy and vibrancy as thermal inkjet printers, especially when printing photographs or graphic-intensive materials. This can be a crucial factor for creative professionals.
3. Bulkiness and Weight: Laser printers tend to be larger and heavier than thermal inkjet printers, which can be a consideration for those with limited space. The size and weight of laser printers can also impact their portability.
Key Considerations When Choosing Between Thermal Inkjet and Laser Printer
When faced with the decision of whether to invest in a thermal inkjet or a laser printer, several key factors should be taken into account to ensure you make the best choice for your specific needs.
1. Print Quality
Print quality is often a primary concern for users, particularly if you require high-quality prints for professional or creative applications. If your primary focus is on producing vibrant color prints—especially for photographs, graphics, or other visually rich documents—a thermal inkjet printer is likely your best option. These printers are adept at delivering exceptional color accuracy, fine detail, and smooth gradients, making them a favorite among photographers and graphic designers.
On the other hand, if your printing needs predominantly involve producing large volumes of text-based documents, a laser printer may be more suitable. Laser printers excel in producing crisp, clear text, which is essential for professional documents, reports, and presentations. The sharpness of text output from a laser printer is often superior to that of thermal inkjet printers.
2. Print Speed
Speed is a crucial factor to consider, especially for offices or environments where time is of the essence. Laser printers typically have a significant advantage in this regard. They are designed to handle high-volume printing tasks efficiently, allowing them to produce pages rapidly. This speed is particularly beneficial in busy office settings, where multiple users may need to print documents simultaneously.
Thermal inkjet printers, however, may struggle with speed, particularly when handling larger print jobs. The slower printing pace can lead to bottlenecks in productivity, especially in environments where quick turnaround times are necessary. If you often find yourself needing quick prints for meetings or presentations, a laser printer would be the more practical choice.
3. Cost of Ownership
When assessing the total cost of ownership, it's important to consider both the initial purchase price and the ongoing costs of consumables, such as ink or toner.
l Thermal Inkjet Printers: While these printers typically have a lower initial purchase price, the cost of replacement ink cartridges can accumulate quickly. If you frequently print documents, the ongoing expense of ink can be a significant consideration that affects your overall budget.
l Laser Printers: Although the initial investment in a laser printer may be higher, they generally offer a lower cost per page due to the longevity of toner cartridges. This can lead to substantial savings over time, especially for businesses or individuals who print frequently.
Ultimately, evaluating the total cost of ownership will help you make a more informed decision based on your budget and printing habits.
4. Media Compatibility
Consider the types of media you plan to print on and how important versatility is for your printing tasks. If you require the ability to print on a wide range of media types—including glossy photo paper, labels, cardstock, and envelopes—a thermal inkjet printer is likely the better choice. These printers can handle various media sizes and types, making them suitable for diverse printing projects.
If your printing needs primarily involve standard office paper, a laser printer should suffice. However, keep in mind that while laser printers can print on specialty media, they may not perform as well as thermal inkjet printers when dealing with non-standard materials.
5. Space and Size
When considering the physical space you have available for a printer, thermal inkjet printers typically have a smaller footprint and are lighter than laser printers. This can be a significant factor if you have limited desk space or if you require a portable printing solution.
Laser printers, due to their larger and bulkier design, may require a dedicated space in your home or office. For users with space constraints or those who need a printer that can be easily moved, thermal inkjet printers may be the more convenient option.
6. Environmental Considerations
Both thermal inkjet and laser printers have environmental impacts, but they differ in significant ways that may influence your decision.
l Thermal Inkjet Printers: These printers often produce less waste in terms of cartridges, especially if you choose to recycle or refill your ink cartridges. However, they may generate more paper waste if print jobs are not managed carefully, particularly in offices where excessive printing occurs.
l Laser Printers: While toner cartridges used in laser printers can be recycled, the fusing process of laser printing consumes more energy than thermal inkjet printing. For environmentally-conscious consumers, this energy consumption may be an important factor to consider.
Conclusion
In the ongoing debate of thermal inkjet vs. laser printer technologies, the right choice ultimately hinges on your specific printing needs and priorities. If you prioritize high-quality color prints, versatility in media handling, and a lower initial investment, a thermal inkjet printer is likely the better option for you. On the other hand, if speed, efficiency, and lower long-term costs are more critical for your environment, a laser printer is probably the more suitable choice.
As you evaluate your typical print volume, the types of documents you frequently produce, and your overall budget, it’s essential to weigh these factors carefully. By doing so, you can ensure that the printer you select will meet your requirements effectively and efficiently, leading to a satisfactory printing experience. Whether you ultimately choose a thermal inkjet printer or a laser printer, making an informed decision will help you achieve your printing goals with ease.